How is manure used on farms?
build these competencies
thinking global
Consider the following global and local perspectives on sustainability and waste.
an agroecosystems approach to livestock farming
Livestock are found in all agroecosystems and include a diverse range of species and breeds raised in a variety of production systems. Livestock play an important role in enhancing food security and nutrition of the public at large and the rural and urban poor in particular by providing access to nutrient dense food, such as meat, milk and eggs.
If managed sustainably, livestock can contribute to important ecosystem functions such as nutrient cycling, soil carbon sequestration and the conservation of agricultural landscapes. They can also improve livelihoods and incomes.
Concerns exist over the impact of the livestock sector on the climate and the environment, the role of livestock in global food security and nutrition, as well as in sustainable and healthy diets and animal health.
Many means of addressing these risks involve optimizing interactions between animals, plants, humans and the environment. These strategies are part of agroecology.
Agricultural productivity, income and resilience can be increased by integrating livestock with other production system components such as trees and crop plants.
By eating fibrous feeds (e.g. grass and straw), livestock make use of biomass that humans cannot eat and increase natural resource use efficiency.
Manure is rich in nutrients and organic matter, which are key to the physical, chemical and biological properties of healthy soils. Good livestock management practices increase plant biodiversity in grasslands, which in turn enhances productivity, resilience, and other ecosystem services.
Adapted from Food and Agriculture Organization (2018). Livestock and agroecology: How they can support the transition towards sustainable food and agriculture. United Nations: Online.
focus on waste prevention
The Food and Agriculture Organization of the UN states that “one-third of food produced for human consumption is lost or wasted globally, which amounts to about 1.3 billion tonnes per year.”
The easiest way to build a more sustainable society is to prevent waste and consume what is produced, whether it is produced through conventional or organic approaches.
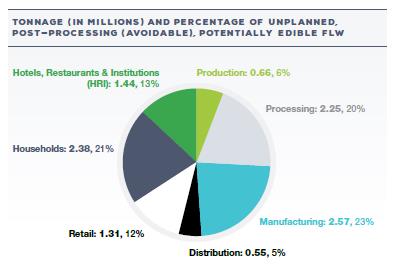
Consider the Canadian statistics, which identifies two types of food loss and waste.
Avoidable includes food loss and waste that may get to retail stores but are not purchased. This unexpected or “unplanned” food loss and waste provides the greatest opportunity to reduce food waste or rescue edible food.
Unavoidable includes by-products that are inedible and thrown out, such as animal bones, husks, and the planned waste that happens when food is cooked and processed. This is expected or “planned” waste.
![]() What conclusions about avoidable and non-avoidable waste can you make from each circle graph?
What conclusions about avoidable and non-avoidable waste can you make from each circle graph?
Used with permission from Nikkel, L. et al. (2019). The Avoidable Crisis of Food Waste: Roadmap. Second Harvest and Value Chain Management International. Online.
A documentary movie called Just Eat It: A Food Waste Story deals with the issue of waste from farm, through retail and all the way to the back of the filmmaker’s own fridges.